Attributes and Associated Operators
The attributes are used to target users. The operators are used to perform operations on user values of different attribute types. Unlaunch support following attributes type and their associated operators are listed below:
String
The String data type has some operators that are used to perform certain operations on string values. The following operators are supported in Unlaunch.
| Operators | Meanings |
|---|---|
| Equals, Not Equal | Exact Match |
| Starts With, Does not Starts With | Prefix String Match |
| Ends With, Does not Ends With | Suffix String Match |
| Contains, Does not Contains | Value match in list |
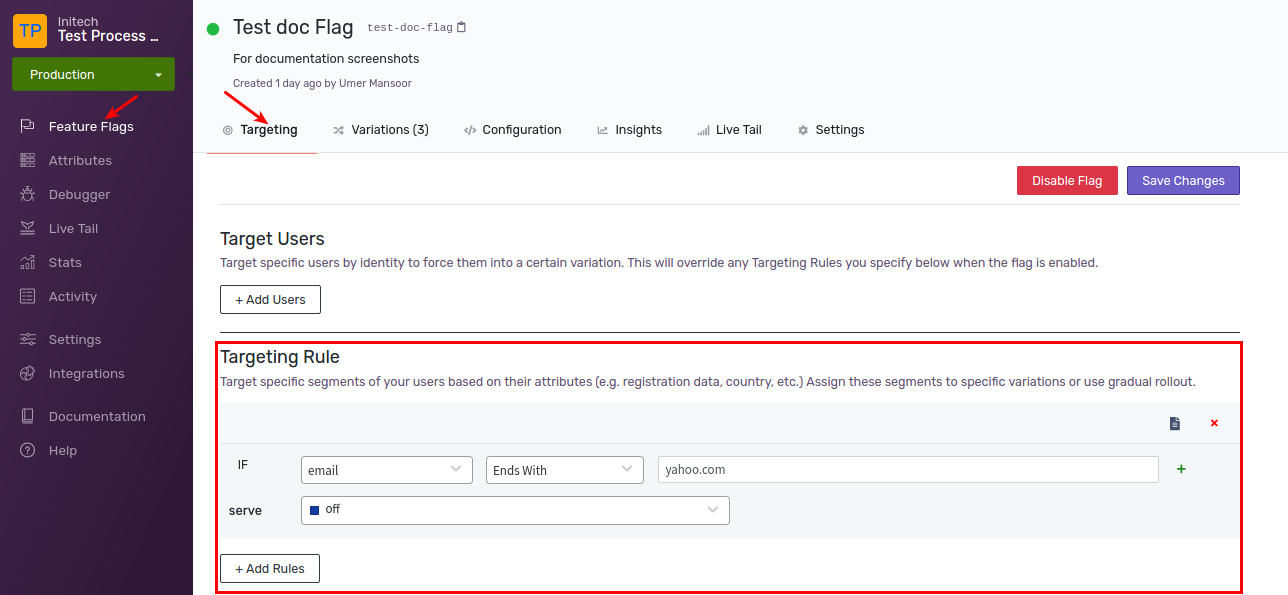
Example 1: Email Ending In yahoo.com
Let’s define a rule that serves off variation to all users whose e-mail address ends with yahoo.com. First, we’ll create a new attribute of type string called email. Then we’ll use the ends with operator, and provide yahoo.com as value. Click Save Changes to save the rule.
Number
Number data type represents both integers and floating point numbers. When comparing numbers, the SDK will convert values you pass at the time of evaluation to the largest floating point type (e.g. Double in Java, float64 in Go) before comparison.
| Operators | Meanings |
|---|---|
| Equals, Not Equal | Exact Match |
| Greater Than | Numeric comparison |
| Greater Than or Equal | Numeric comparison |
| Less Than | Numeric comparison |
| Less Than or Equal | Numeric comparison |
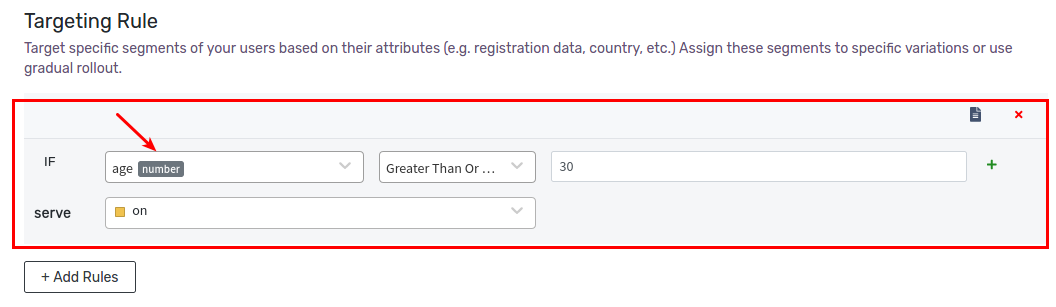
Example 2: Age Greater Than 30
Let’s define a rule that serves on variation to all users whose age is greater than or equals to 30. First, we’ll create a new attribute of type number called age. Then we’ll use the Greater Than or Equals operator, and provide 30 as value. Click Save Changes to save the rule.
Boolean
For the Boolean datatype, the following operators are supported.
| Operators | Meanings |
|---|---|
| Equals, Not Equal | Exact Match |
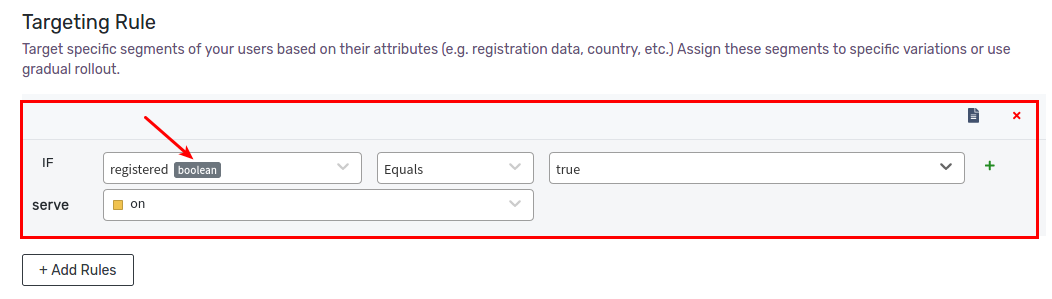
Example 3: If User is Registered (True)
Let’s define a rule that serves on variation to all users whose registered value equals true. First, we’ll create a new attribute of type boolean called registered. Then we’ll use the Equals operator, and provide true as value. Click Save Changes to save the rule.
DateTime
DateTime data type represents a date and time. The following operators are supported. All date and time comparisons are done in UTC. When you provide a date and time value in the Unlaunch Console, it is assumed to be in UTC.
| Operators | Meanings |
|---|---|
| Equals, Not Equal | Exact Match |
| Greater Than | date comparison |
| Greater Than or Equal | date comparison |
| Less Than | date comparison |
| Less Than or Equal | date comparison |
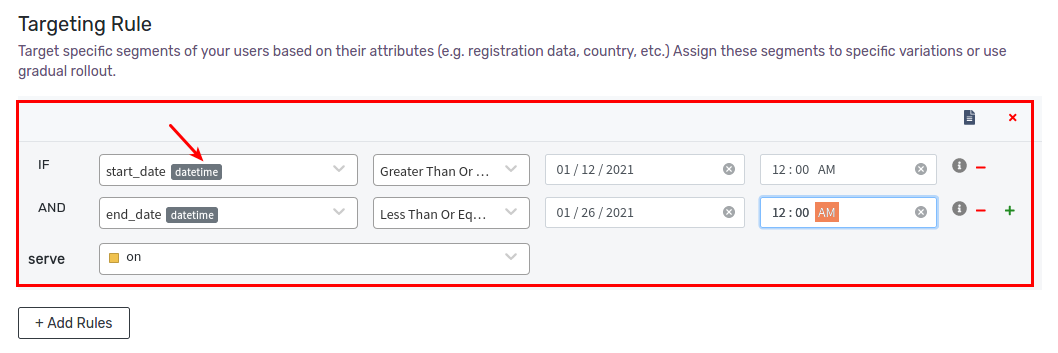
Example 4: Start_Date Is today and End_Date Is After 2 Weeks
Let’s define a rule that serves on variation to all users whose start-date greater than or equals 01/12/2021 12:00:AM and end-date less than or equals 01/26/2021 12:00:AM. First, we’ll create two new attribute of type datetime called start_date and end_date. Then we’ll use the Greater Than or Equals and Less Than or Equals operator, and provide two datetime values. Click Save Changes to save the rule.
Date
Date data type represents a date (without time). The following operators are supported. All date comparisons are done in UTC.
| Operators | Meanings |
|---|---|
| Equals, Not Equal | Exact Match |
| Greater Than | date comparison |
| Greater Than or Equal | date comparison |
| Less Than | date comparison |
| Less Than or Equal | date comparison |
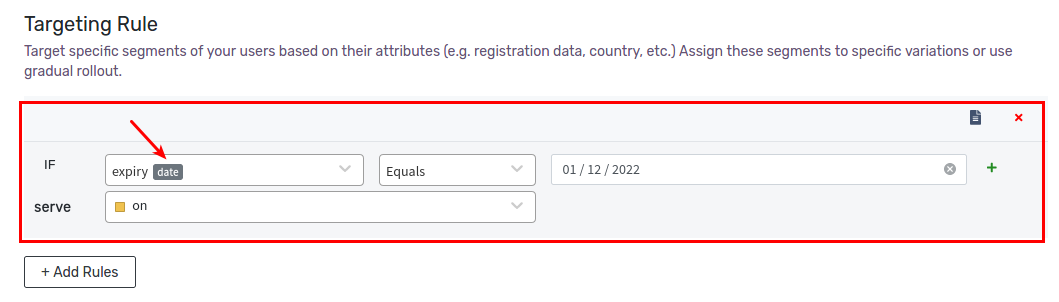
Example 5: Expiry Date Equals 01/12/2022
Let’s define a rule that serves on variation to all users whose expiry equals 01/12/2022. First, we’ll create a new attribute of type date called expiry. Then we’ll use the Equals operator, and provide 01/12/2022 as value. Click Save Changes to save the rule.
Set
A Set data type is a collection of elements. The following operators are supported. All set operators assume individual elements of the set are strings. For example, [1] == [1] but [1] != [1.0] because 1 != 1.0
| Operators | Meanings |
|---|---|
| Equals, Not Equal | Exact Match |
| Is Part of, Is not Part of | Subset of a set match |
| Has Any of, Does not Have Any of | Matches any of |
| Has All of, Does not Have All of | Matches all of |
Examples
| Targeting Rule | Will Match |
|---|---|
Equals (USA,CAN) |
(USA,CAN) |
Is Part of (USA,CAN,MEX) |
(USA,CAN) |
Has Any of (IND,PAK) |
(PAK) or (IND) |
Has All of (DEU,AUT) |
(DEU,AUT) |
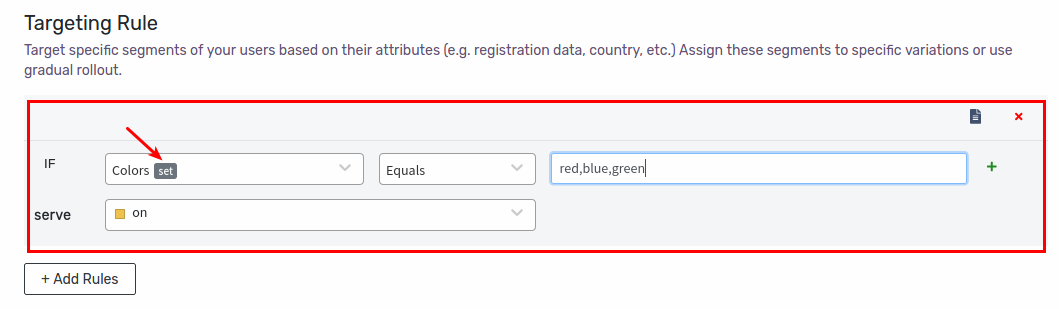
Example 6: Color Set contains (red,blue,green)
Let’s define a rule that serves on variation to all users whose colors equals (red,blue,green). First, we’ll create a new attribute of type set called colors. Then we’ll use the equals operator, and provide (red,blue,green( as value. Click Save Changes to save the rule.